As organizations strive to safeguard their sensitive data and critical assets, multi-factor authentication (MFA) has emerged as a popular choice for enhancing security. However, as recent high-profile attacks have shown, relying solely on MFA for authentication can leave organizations vulnerable to cyber threats. In this article, we will delve into the various weaknesses of MFA, highlight notable incidents that exploited these weaknesses, and explore how pairing MFA with digital certificates can provide a more secure authentication solution.
The Rise and Limitations of Multi-Factor Authentication
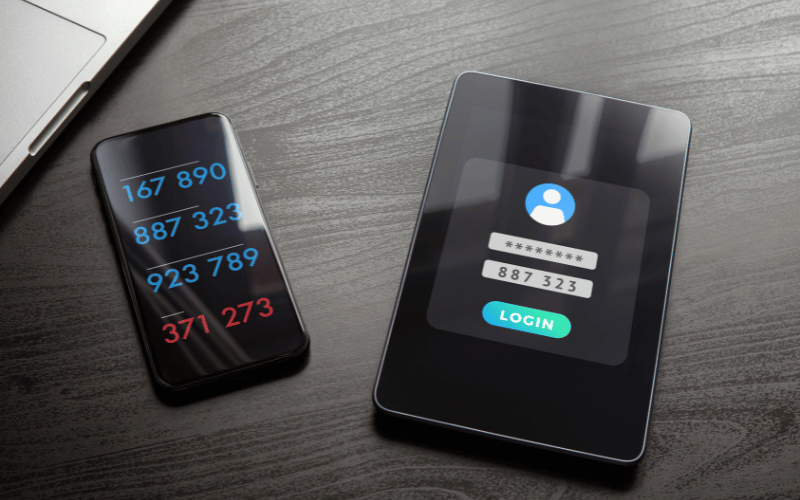
Multi-factor authentication, as the name suggests, combines multiple forms of verification to grant access to systems and data. It typically involves something you know (like a password), something you have (like a smartphone or token), and something you are (like a fingerprint or facial recognition). This layered approach adds an extra layer of security beyond traditional username-password combinations, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
However, MFA is not without its vulnerabilities:
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing remains a prevalent attack vector, and even MFA cannot fully protect against it. In a phishing attack, cybercriminals trick users into revealing their credentials or MFA codes by masquerading as a legitimate entity. Once the attacker has both the password and the MFA code, they can gain access just as easily as the legitimate user.
- SIM Swapping: In SIM swapping attacks, hackers fraudulently transfer a victim’s phone number to a new SIM card, allowing them to intercept MFA codes sent via SMS. This technique has been used successfully to compromise high-profile social media and cryptocurrency accounts.
- Biometric Vulnerabilities: While biometric factors like fingerprints and facial recognition provide an added layer of security, they are not foolproof. Sophisticated attackers have demonstrated the ability to bypass these mechanisms using techniques such as fingerprint replication or deepfake technology.
- MFA Code Interception: Even if MFA codes are generated by authenticator apps or hardware tokens, they can still be intercepted if the user’s device is compromised by malware or if the token is stolen. This highlights the importance of securing the device itself.
High-Profile MFA Exploits
Over the past few years, several high-profile incidents have demonstrated the limitations of MFA:
- Twitter Hack (2020): In a widely publicized attack, hackers compromised several high-profile Twitter accounts, including those of Barack Obama, Elon Musk, and Bill Gates. While MFA was enabled on these accounts, the attackers used social engineering techniques to manipulate Twitter employees into granting them access to internal tools, effectively bypassing MFA.
- SolarWinds Attack (2020): The SolarWinds supply chain attack, one of the most significant cyber incidents in recent memory, highlighted the vulnerability of MFA. Attackers compromised SolarWinds’ software updates and used them to distribute malware to thousands of organizations. Once inside these networks, the attackers could bypass MFA using stolen credentials.
Beyond MFA: Going Passwordless with Digital Certificates
To address the limitations of MFA, organizations are turning to digital certificates as a complementary, passwordless authentication method. Digital certificates provide a secure means of identifying both users and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Here’s an overview of how digital certificates enhance authentication:
- Strong Authentication Digital: Digital certificates use asymmetric cryptography, making them extremely secure. Users and devices are issued a unique certificate that includes a public and private key pair. When they attempt to access a system, the private key is used to sign a challenge from the server. This challenge-response process ensures that only the legitimate certificate holder can gain access.
- Device Authentication: Certificates can also be used to authenticate devices, not just users. This is particularly valuable in the context of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, where traditional username-password authentication is often impractical.
- Secure Key Management: Certificates are stored securely, typically in hardware security modules (HSMs), making it difficult for attackers to compromise them. This level of protection is often superior to the security of user-generated passwords and MFA tokens.
- Reduced Phishing Risk: Since digital certificates are based on cryptographic keys rather than static credentials like passwords or codes, they are not susceptible to phishing attacks. Even if an attacker gains access to a user’s certificate, they would still need the private key to authenticate.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, are subject to strict regulatory requirements for data protection. Digital certificates help organizations meet these compliance standards by providing a robust authentication mechanism.
Employing a Multi-Layered Approach to Cybersecurity
While multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a valuable component of a cybersecurity strategy, it is not a silver bullet. Recent high-profile attacks have demonstrated its limitations, particularly in the face of sophisticated threats. To bolster their defenses, organizations should consider adopting a multi-layered approach that combines MFA with digital certificates.
Digital certificates offer strong, cryptographic authentication that is less susceptible to common attack vectors like phishing. They provide a secure means of identifying both users and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. By integrating digital certificates into their authentication systems, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect their critical IT assets from evolving threats.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying one step ahead of adversaries is crucial. By recognizing the limitations of MFA and embracing more robust authentication methods like digital certificates, organizations can better safeguard their valuable data and maintain the trust of their stakeholders in an increasingly interconnected world.
Try Portnox Cloud for Free Today
Gain access to all of Portnox's powerful zero trust access control free capabilities for 30 days!




